WHAT IS A WORK ACCIDENT?
According to Article 11/A of the SSK Law, it is an event that occurs in one of the following situations and conditions and causes the insured to become physically or mentally disabled immediately or later. During the time spent by the employer on duty to another place due to the work carried out by the employer while the insured is at the workplace, during the time spent by the nursing female insured to breastfeed her child, during the collective transportation of the insured to the place of work in a vehicle provided by the employer.
According to TS 18001, Occupational Health and Safety are the conditions and factors that affect or may affect the health and safety of employees or other workers, visitors and other people in the workplace.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF TS 18001 OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM?
It reduces illness and disability, thus improving employees and society. It provides added value and money savings through efficient allocation of resources. It ensures that possible hazards that may result in harm are detected in advance and necessary precautions are taken.
Employees are protected from the negative effects of the workplace and are provided with a comfortable and safe environment to work in. Employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction and reduction in production costs are ensured. The very high costs of work accidents and occupational diseases are minimized.
COSTS OF ACCIDENTS
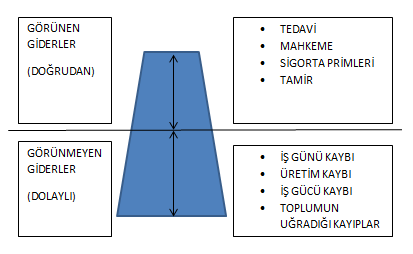
WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF WORK ACCIDENTS?
- SOCIOLOGICAL
- PSYCHOLOGICAL
- MEDICAL
- ECONOMIC
For the employee, it may result in disability or loss of life.
From the employer's perspective, production and efficiency are negatively affected.
In terms of the country's economy; the social security system is damaged, the country's resources are wasted and national welfare is negatively affected.
WHAT ARE THE FACTORS AFFECTING HEALTH?
1. PERSONAL FACTORS: Eating habits and hygiene habits.
2. ENVIRONMENT: Physical Environment (heat, cold, ventilation)
3. Biological Environment (agriculture, animal husbandry, bacteria, microorganisms)
4. Social Environment (traditions, culture, beliefs)
5. Psychological Environment (absent-mindedness, nervousness, indifference, carelessness)
6. OTHER FACTORS: Hereditary
DEFINITIONS AND Definitions
Acceptable Risk: Risk reduced to the level that the organization can tolerate in accordance with its legal obligations and its own OHS policy.
Examination: The systematic, independent and documented process for obtaining and objectively evaluating “audit evidence” to determine the degree to which “audit criteria” are met.
Danger : A source, situation or process that may cause injury or ill health to people or a combination of these.
Event : Work-related events that cause, or have the potential to cause, injury or ill health or death.
Occupational Health and Safety: Conditions and factors that affect or are likely to affect the health and safety of employees or other workers, visitors and other people in the workplace.
Occupational Health and Safety Management System: Part of the overall organization's management system used to develop and implement the organization's OSH policy and manage OSH risks.
Risk : The combination of the probability of a hazardous event or exposure occurring and the severity of injury or ill health that the event or exposure may cause.
HOW TO ESTABLISH AN OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM?
1. PLANNING PHASE: All goals and objectives of the organization are determined and implementation methods are developed.
2. ACTIVITY PHASE: The plan is implemented and agreed upon measures are taken in line with the organization's objectives.
3. EVALUATION PHASE: Activities within the plan are checked for effectiveness and adequacy, and the results are compared with the plan.
4. CORRECTIVE ACTION PHASE: Identified deficiencies are eliminated, the plan may be revised according to changing conditions, and procedures are restructured as necessary.
WHAT ARE THE OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM CONDITIONS?
1. GENERAL CONDITIONS
2. OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY POLICY
3. PLANNING
4. IMPLEMENTATION AND OPERATION
5. CONTROL
6. MANAGEMENT REVIEW
1. GENERAL CONDITIONS
The organization must establish, document, maintain and continually improve an OHS management system in accordance with the requirements of this OHS standard and determine how the OHS management system will meet these requirements.
The organization must describe and document the scope of the OSH management system.
2. OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY POLICY
The OSH policy should ensure that: It is appropriate to the nature and magnitude of the organisation’s OSH risks. It should include a commitment to prevent injuries and ill health and to continuously improve OSH management and OSH performance. It should provide a framework for setting and reviewing OSH objectives. It should be documented, implemented and maintained. It should be communicated to all employees under the organisation’s control so that employees are aware of their individual OSH responsibilities. It should be accessible to interested parties. It should be reviewed periodically to ensure that it remains relevant and appropriate to the organisation.
Topics that can be covered in the OHS policy are; reducing accidents, safe working environment, reducing risks, training and participation of employees, importance given to health workers, compliance with the law, continuous development.
3. PLANNING
a) Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment and Determination of Controls
The organization must establish and maintain procedures to identify hazards, assess risks and determine necessary controls on an ongoing basis.
Risk assessment should be preventive rather than corrective and is divided into corrective and preventive.
In corrective risk assessment, it is envisaged that risk assessment will be carried out and control measures will be initiated after activities and procedures are established and changes are implemented.
In preventive risk assessment, it is envisaged to conduct risk assessment and take precautions before implementing changes and activities.
The basic principle in control measures that can be taken is to eliminate the risk. If the risk cannot be eliminated, it should be reduced and protective equipment should be used at a later stage.
The control methods that can be taken are divided into 3; Engineering Control: Equipment and facility design, creation of processes that eliminate hazards.
Managerial Control: Creating documents such as procedures, instructions, etc., granting work permits, restricting working hours, warning signs, training.
Personal Protective Equipment: Gloves, headgear, earplugs, work clothes
Business activities are divided into 5 parts; Continuous Work: Production, painting, Infrequent Work: Maintenance, cleaning, Heavy and Dangerous Work, Work done inside the company site, Work done outside, Chemical, Mechanical, Biological, Electrical Activities.
Hazard classes are as follows; Hazards Caused by Gravity
Falling from height, falling into a pit, falling pieces, slipping, stumbling, tripping, burning-scalding
Burning with flames, hot surfaces, hot liquids, steamFire-Explosion
Flammable gas, steam, natural gas, LPG, flammable liquid, flammable solids, flammable dust, flammable chemicals, cigarettes Environmental and Natural Hazards
Earthquake, flood, storm, lightning, snow, extreme heat/coldPressure Systems
Compressed gases, compressed air, vacuum Machinery-Equipment Hazards
Moving parts, getting caught in rotating equipment, sharp edges, flying, breaking, scattered parts Electrical Hazard
High voltage, damaged cables and sockets, overloaded circuits, inappropriate panels
Dangers of Transport-Lifting Vehicles
Electrical Hazard
Overloading of cranes, forklifts and pallet trucks, vehicle traffic, elevators
Biological Hazards
Laboratory work, foodborne diseases, bloodborne diseases Chemical Hazards
Carcinogenic, corrosive, abrasive, irritant, toxic Ergonomic Hazards
Strainful positions, repetitive movements, prolonged static positionsTransportation HazardsRadiation Hazards
b) Legal and Other Conditions
The organization should be aware of how relevant legal and other requirements affect its operations or how they may affect it in the future, and should communicate this information to relevant personnel.
Some Turkish Business Legislations are below;
- Labor Law
- Social Security Law
- Occupational Health and Safety Regulation
- Machinery Safety Regulation
- Regulation on the Transport of Dangerous Goods by Road
- Hazardous Chemicals Regulation
- Noise Control Regulation
- Earthing Regulation in Electrical Installations
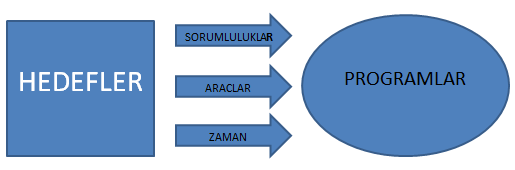
c) Objectives and Programs
The organization should try to achieve its OHS policy and goals by creating an OHS program. For this, strategies and action plans should be developed. These strategies and action plans should be documented and published. Progress towards achieving OHS goals should be monitored, reviewed and recorded. Accordingly, strategies and action plans should be updated or changed when necessary.
The organization must establish, implement and maintain documented occupational health and safety objectives at each relevant function and level within the organization.
Objectives should be expressed in measurable quantities where practical and should be consistent with the OSH policy.
Goals should be set to ensure continuous improvement.
4. IMPLEMENTATION AND OPERATION
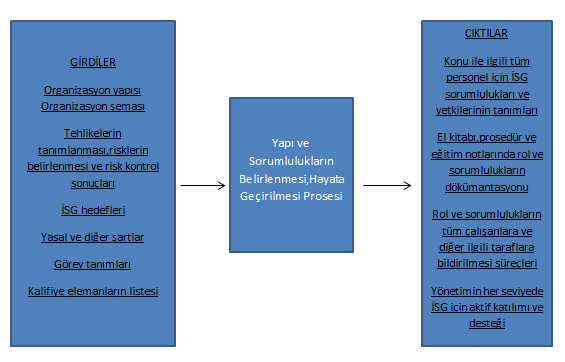
a) Resources, Duties, Responsibility, Accountability and Authority
b) Education, Awareness and Competence
The organization must ensure that personnel performing tasks under its control that may affect OSH in the workplace are competent in terms of appropriate education, training or experience and maintain relevant records.
The organization must determine the need for training on OSH risks and the OSH management system. The organization must provide training or take measures to meet this need, evaluate the effectiveness of the training or measures taken and keep records of this.
There are 3 types of training;
Trainings for All Employees:First AidFire Protection and PreventionSafe Use of Liquid Chemicals and Gases
System Oriented Trainings:Accident AssessmentManagement of Hazardous and Harmful SubstancesWarning SignsStakeholder Information
Work-Specific Trainings: General Work Safety Manual Load Lifting Techniques Natural Gas Crane Signaling Adaptation Trainings In-Unit Training System Manuals
c) Communication, Participation and Consultation
The organization shall establish, implement and maintain procedures for the following in relation to OSH hazards and the OSH management system: Internal communication across the organization's various levels and functions Communication with contractors and other visitors to the workplace Receiving, documenting and responding to relevant communications from external interested parties
The organization shall encourage all those affected by its operations to participate in its OH&S practices and support its OH&S policy and OH&S objectives through a consultation and communication process.
d) Documentation and Document Control
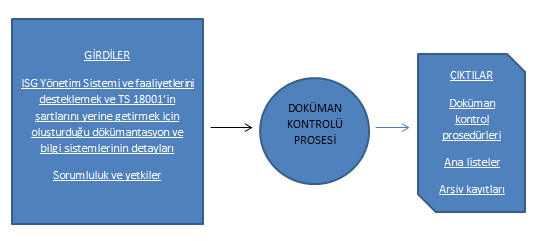
e) Business Control
The organization shall establish and maintain arrangements to ensure the effective application of controls and countermeasures when necessary to control operational risks, implement the OSH policy, achieve OSH objectives and comply with legal and other requirements.
f) Emergency Preparations and What to Do in Such Cases
The organization must be able to identify potential emergency situations and ensure that necessary actions are taken in such emergencies.
Emergency plans should be as follows; Definition of the emergencyDescription of the personnel who will be on dutyResponsibilities and authorities of the personnel who will be on dutyWhat will happen to hazardous materials in emergenciesInternal and external communicationProtection of vital equipmentEmergency equipmentEvacuation of the emergency scene
Emergency equipment includes: Alarm systems, emergency lighting and power, escape routes, assembly points, shelter, critical isolation valves, switches and breakers, fire equipment, first aid supplies, communication devices.
Drills should be conducted on a schedule, external assistance should be encouraged, the functionality of emergency plans should be tested, malfunctions should be detected, and emergency equipment should be checked.
5. CONTROL
a) Performance Measurement and Monitoring
b) Evaluation of Suitability
c) Accidents, Incidents, Nonconformities, Corrective and Preventive Activities
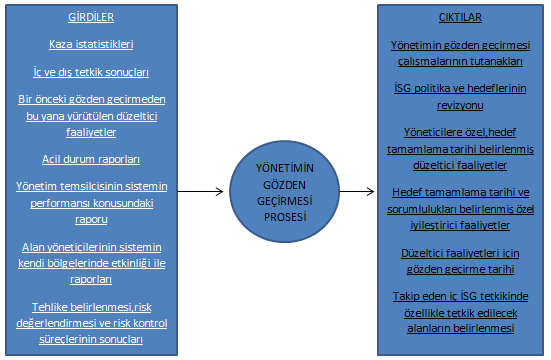
6. MANAGEMENT REVIEW